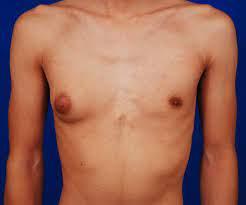
Gynecomastia, a condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, is more common than often realized. Despite its prevalence, many individuals remain unaware of its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of gynecomastia to provide clarity and understanding.
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a medical condition that results in the swelling of breast tissue in males. It can occur at any age and is often characterized by an increase in the size of one or both breasts. While it is not a serious health threat, gynecomastia can cause significant psychological distress and affect self-confidence and quality of life.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Several factors can contribute to the development of gynecomastia, including hormonal imbalances, certain medications, and underlying health conditions.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances, particularly an increase in estrogen levels relative to testosterone, are a common cause of gynecomastia. This imbalance can occur during puberty, leading to temporary breast enlargement in teenage boys. Additionally, hormonal changes associated with aging, such as a decrease in testosterone production, can also contribute to gynecomastia in older men.
Medications
Certain medications have been linked to the development of gynecomastia as a side effect. These include:
- Anti-androgens: Drugs used to treat prostate enlargement and prostate cancer can interfere with hormone levels, leading to breast enlargement.
- Anabolic steroids: Abuse of anabolic steroids, often used by bodybuilders and athletes to enhance performance, can disrupt hormone balance and result in gynecomastia.
- Some antidepressants and antipsychotics: Certain psychiatric medications may cause gynecomastia as a side effect.
Underlying Health Conditions
In some cases, gynecomastia may be a symptom of an underlying health condition, such as:
- Hypogonadism: A condition in which the body doesn't produce enough testosterone, leading to hormonal imbalances.
- Hyperthyroidism: Overactivity of the thyroid gland can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to breast enlargement.
- Liver or kidney disease: Dysfunction of the liver or kidneys can affect hormone metabolism and lead to gynecomastia.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
The primary symptom of gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue, which may be accompanied by tenderness or sensitivity. It is essential to distinguish gynecomastia from other conditions, such as pseudogynecomastia, which refers to the accumulation of fat in the chest area without glandular enlargement.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
The treatment approach for gynecomastia depends on its underlying cause, severity, and the presence of any associated symptoms. Treatment options may include:
Observation and Monitoring
In cases where gynecomastia is mild and not causing significant discomfort or distress, a conservative approach of observation and monitoring may be recommended. This involves regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider to assess any changes in breast size or symptoms.
Medications
Certain medications may be prescribed to help reduce breast tissue or alleviate symptoms associated with gynecomastia. These may include:
- Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs): Drugs such as tamoxifen or raloxifene can help block the effects of estrogen on breast tissue and reduce breast size.
- Aromatase inhibitors: Medications that inhibit the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen, may be used to rebalance hormone levels.
Surgery
In cases of severe or persistent gynecomastia that does not respond to conservative measures or medication, surgical intervention may be considered. Male breast reduction surgery, also known as mastectomy or liposuction, involves the removal of excess breast tissue and reshaping the chest contour to achieve a more masculine appearance.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia is a common condition that can have significant physical and psychological effects on affected individuals. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions about managing gynecomastia and improving their quality of life.