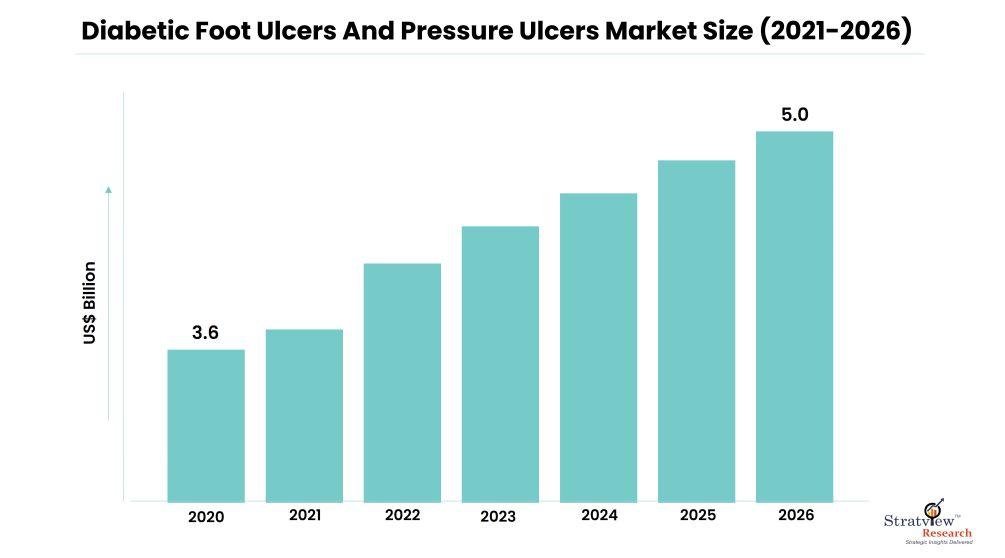
Diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers are significant health concerns affecting millions of people worldwide. These chronic wounds pose serious complications, leading to increased morbidity, prolonged hospital stays, and high healthcare costs. However, with the rapid advancement of technology, the healthcare industry has witnessed remarkable innovations and emerging technologies in the field of diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcer management. These innovations are revolutionizing wound care, promoting faster healing, and improving patient outcomes. The diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers market is estimated to grow from USD 3.6 billion in 2020 to USD 5.0 billion by 2026 at a healthy CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period.
One of the most promising technologies in diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcer management is the use of advanced dressings and wound care products. Traditional wound dressings are being replaced by sophisticated dressings that provide an optimal wound environment, enhance moisture control, and promote tissue regeneration. These advanced dressings, such as hydrogels, foams, and films, possess superior absorption capabilities and facilitate faster healing. Additionally, the incorporation of antimicrobial agents in dressings helps to prevent infection, a common complication in chronic wounds.
Another significant innovation is the development of smart wound monitoring systems. These technologies employ various sensors and imaging techniques to provide real-time data on wound status and progress. For instance, smart dressings equipped with sensors can monitor temperature, pH levels, and moisture content in the wound bed, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the healing process accurately. Furthermore, advanced imaging technologies like infrared thermography and hyperspectral imaging enable early detection of wound infections and tissue abnormalities, aiding in prompt intervention and preventing complications.
The emergence of regenerative medicine has also transformed the diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers market. Stem cell therapy, for example, shows immense potential in promoting wound healing. Stem cells derived from various sources, such as bone marrow or adipose tissue, are applied directly to the wound site, stimulating tissue regeneration and angiogenesis. This cutting-edge approach accelerates wound closure and reduces the risk of infection. Moreover, tissue engineering techniques have led to the development of bioengineered skin substitutes that can be applied to large and complex wounds, providing a scaffold for tissue growth and facilitating wound closure.
Innovations in offloading devices have also made a significant impact on the management of diabetic foot ulcers. Pressure redistribution is crucial in preventing and treating these ulcers. Newer offloading technologies, such as wearable pressure sensors, pressure-sensing insoles, and custom-made orthotics, help to relieve pressure on the affected area, reduce friction, and improve gait. These devices not only enhance patient comfort but also reduce the risk of ulcer recurrence.
Telemedicine and digital health solutions have become indispensable tools in the management of chronic wounds. Remote patient monitoring and teleconsultations allow healthcare professionals to assess wounds, provide guidance, and make timely interventions without the need for in-person visits. Patients can capture and share images of their wounds through smartphone apps, facilitating regular assessments and enabling healthcare providers to track progress. Such technology-driven solutions not only improve accessibility to care but also enhance patient compliance and reduce healthcare costs.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms into wound care systems has revolutionized decision-making and personalized treatment plans. These technologies analyze vast amounts of patient data, including medical history, wound characteristics, and treatment outcomes, to provide evidence-based recommendations. AI-powered algorithms can predict wound healing trajectories, identify high-risk patients, and suggest optimized treatment strategies, leading to better clinical outcomes and resource utilization.
In conclusion, emerging technologies and innovations are transforming the diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers market. From advanced wound dressings and smart monitoring systems to regenerative medicine and telemedicine, these advancements are revolutionizing wound care, improving patient outcomes, and reducing the burden on healthcare systems. With ongoing research and development, we can expect further breakthroughs in the field, ultimately leading to more effective prevention, management, and treatment of chronic wounds