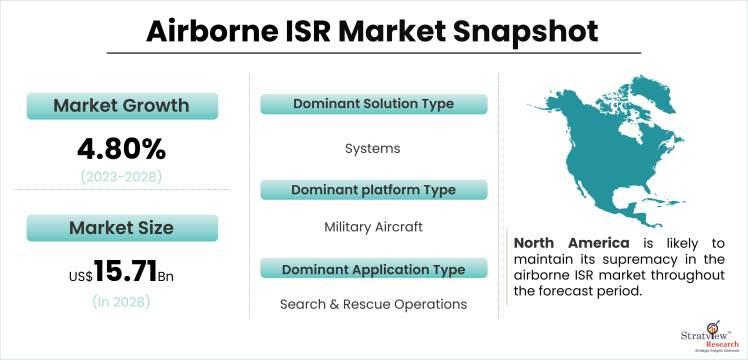
Airborne Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities are undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by emerging technologies that promise to revolutionize the field. As modern warfare continues to evolve, advancements in sensor systems, data processing, and communication technologies are shaping the future of airborne ISR. This article explores some of the key emerging technologies that are poised to have a significant impact on the effectiveness and efficiency of airborne ISR operations. The airborne ISR market is estimated to grow from USD 10.45 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 4.9% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 13.96 billion by 2028.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning technologies are revolutionizing airborne ISR by enabling advanced data processing and analysis. By leveraging AI algorithms, ISR platforms can autonomously analyze vast amounts of sensor data in real-time, identifying patterns, detecting anomalies, and highlighting relevant information for human operators. This capability significantly enhances the speed and accuracy of data interpretation, allowing for more informed decision-making and rapid response to evolving situations.
Hyperspectral Imaging:
Hyperspectral imaging is an emerging technology that provides detailed and highly specific information about the composition of objects and materials on the ground. By capturing images across a wide range of the electromagnetic spectrum, hyperspectral sensors can identify subtle differences in the reflectance of various materials. This capability has significant applications in airborne ISR, allowing for improved target identification, environmental monitoring, and the detection of concealed or camouflaged objects.
Quantum Sensors:
Quantum sensors, based on the principles of quantum physics, have the potential to revolutionize airborne ISR by offering unprecedented levels of sensitivity and precision. These sensors can detect and measure extremely small changes in physical quantities, such as gravity, magnetic fields, or time, enabling highly accurate positioning, navigation, and target tracking. Quantum sensors promise enhanced situational awareness and increased reliability, particularly in challenging operational environments.
Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) Swarm Technology:
The concept of UAS swarm technology involves the coordinated operation of multiple unmanned aerial systems to accomplish complex missions. Swarm technology holds immense potential in airborne ISR, allowing for increased coverage, redundancy, and resilience. By leveraging autonomous algorithms, swarms of UAS can collaborate in real-time, sharing information and performing coordinated intelligence-gathering tasks. This technology promises to overcome limitations of individual platforms and offers greater flexibility and adaptability in dynamic battlefield scenarios.
Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) Operations:
Traditionally, airborne ISR platforms have operated within the visual line of sight of operators. However, advancements in communication systems, command and control infrastructure, and regulatory frameworks are enabling the expansion of beyond visual line of sight operations. BVLOS capabilities allow ISR platforms to cover larger areas, operate in remote or hostile environments, and conduct prolonged surveillance missions. This technology opens up new possibilities for extended-range reconnaissance, persistent surveillance, and rapid response capabilities.
Conclusion:
The future of airborne ISR is being shaped by a range of emerging technologies that promise to enhance the capabilities, efficiency, and effectiveness of intelligence-gathering operations. From the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for data analysis to the advancements in hyperspectral imaging, quantum sensors, UAS swarm technology, and BVLOS operations, these technologies are poised to revolutionize the way ISR missions are conducted. By leveraging these advancements, military forces can gain unprecedented situational awareness, improve decision-making, and respond rapidly to emerging threats on the battlefield. It is essential for defense organizations to invest in research and development and foster collaborations to harness the full potential of these emerging technologies and stay ahead in an increasingly complex and dynamic operational environment.