Post Market Surveillance (PMS) is a crucial aspect of the life cycle of medical devices. It is the process of systematically monitoring the safety and performance of medical devices once they are on the market and in the hands of patients and healthcare professionals. PMS plays a vital role in identifying and addressing any issues or potential risks associated with medical devices, thereby ensuring patient safety and maintaining public trust in the healthcare system. This article explores the significance of post-market surveillance, its objectives, methodologies, and the impact it has on the medical device industry.
Objectives of Post-Market Surveillance
-
Early Detection of Adverse Events: PMS helps in the early detection of adverse events, including device malfunctions, complications, or unexpected side effects. Identifying such events promptly allows for timely interventions and appropriate risk mitigation measures.
-
Assessing Device Performance: Monitoring devices in real-world settings provides valuable insights into their performance outside the controlled environment of clinical trials. It allows manufacturers to evaluate if the devices meet their intended performance claims and make any necessary improvements.
-
Identifying Emerging Safety Issues: As medical devices are used in a broader patient population, rare or long-term safety issues may arise. PMS helps in identifying and understanding these emerging safety concerns, contributing to more informed decision-making.
Methodologies for Post-Market Surveillance
-
Adverse Event Reporting: Healthcare providers, patients, and manufacturers can report adverse events associated with medical devices to regulatory authorities or the manufacturers themselves. These reports are critical in identifying potential safety issues.
-
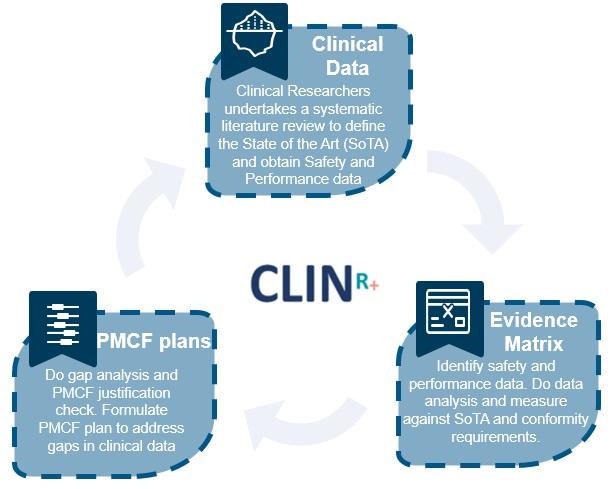
Post-Market Clinical Follow-up (PMCF): Manufacturers conduct PMCF studies to collect additional clinical data on device safety and performance beyond what was gathered during pre-market clinical trials. PMCF studies are often required by regulatory authorities to ensure ongoing assessment of device safety.
-
Device Registries: Some countries maintain national or international device registries to collect and analyze data on medical devices' safety and effectiveness over time. These registries are valuable sources of real-world evidence for PMS.
Impact on the Medical Device Industry
-
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with post-market surveillance requirements is essential for medical device manufacturers. Regulatory authorities worldwide, such as the U.S. FDA and the European Union's Notified Bodies, require manufacturers to have robust post-market surveillance systems in place as a condition for maintaining market access.
-
Risk Mitigation and Product Improvements: Through PMS, manufacturers can identify and address safety concerns promptly, leading to necessary risk mitigation measures and product improvements. This ensures that devices remain safe and effective throughout their lifecycle.
-
Patient Safety and Public Trust: By proactively monitoring device performance, addressing safety issues, and communicating transparently with patients and healthcare providers, PMS enhances patient safety and helps maintain public trust in the medical device industry.
Conclusion
Post-Market Surveillance is a critical component of the medical device life cycle, focusing on the ongoing monitoring of device safety and performance once devices are in use. Its primary objectives are to detect adverse events early, assess device performance, and identify emerging safety issues. By employing various methodologies such as adverse event reporting, PMCF studies, and device registries, manufacturers can ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, mitigate risks, and continuously improve device safety and effectiveness. Ultimately, post-market surveillance plays an indispensable role in safeguarding patients and upholding the credibility of the medical device industry.